Generative AI Takes Center Stage in Hiring: A Deep Dive into AI-Powered Interviews and Recruitment
The landscape of talent acquisition is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the rapid advancements and widespread adoption of artificial intelligence, particularly generative AI (genAI). What was once a futuristic concept is now firmly embedded in the everyday operations of human resources and hiring departments across the globe. A recent report sheds light on just how quickly this shift is occurring, revealing that a significant portion of employers are already leveraging AI for one of the most critical stages of the hiring process: the initial candidate interview.
AI Interviews: From Fringe to Mainstream
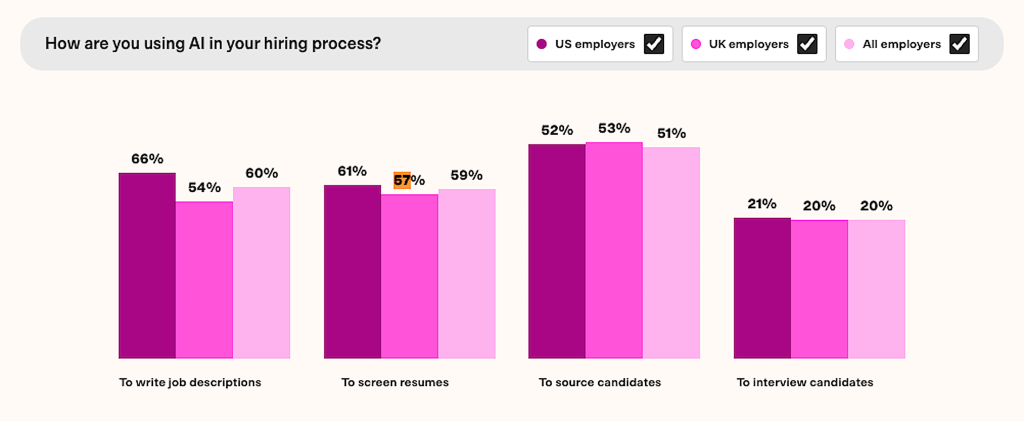
According to the State of Skills-Based Hiring 2025 report by TestGorilla, an Amsterdam-based pre-employment testing platform, approximately one in five employers in both the United States (21%) and the United Kingdom (20%) are now utilizing generative AI tools to conduct initial interviews with prospective hires. This statistic is a powerful indicator that AI-based hiring is no longer an experimental endeavor confined to early adopters; it has become a mainstream practice.
Wouter Durville, CEO and Co-Founder at TestGorilla, commented on this trend, stating, “Right now, AI is mainly a screening tool, not a decision-maker — most commonly for writing job descriptions, screening resumes, and sourcing candidates. But we’re also seeing a sharp rise in AI-led interviews, with 21% of US employers now using them. That’s a clear sign these tools are moving quickly from the fringes to the mainstream.”
This integration of AI into interviews signifies a growing confidence among employers in the technology's ability to handle candidate interactions, at least in the preliminary stages. It suggests a recognition of AI's potential to streamline processes, increase efficiency, and potentially improve the quality of hires.

The Broader Role of GenAI in Recruitment
While AI interviews are a notable development, generative AI's influence extends across the entire recruitment lifecycle. The TestGorilla report indicates that a significant majority of employers (70%) are using genAI in some capacity within their hiring processes. Beyond interviews, the most common applications include:
- Writing job descriptions (66% of US employers)
- Screening resumes (61% of US employers)
- Sourcing candidates (52% of US employers)
These applications highlight AI's current strength as an automation and efficiency tool. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks like drafting job descriptions or sifting through vast numbers of resumes, AI frees up human recruiters to focus on more strategic activities, such as building relationships with candidates, conducting deeper evaluations, and making final hiring decisions.
Lisa Rowan, a vice president of human capital management research at IDC Research, notes that genAI-based talent acquisition software spans various areas, from job marketing (like Beamery) to applicant tracking systems (such as iCIMS, Jobvite, Smartrecruiters, SAP SuccessFactors, Oracle, and Workday) and data analysis platforms (including Modern Hire, Seekout, Eightfold, and Phenom).
The Shift Towards Skills-Based Hiring
The rise of AI in hiring is intrinsically linked to a broader strategic shift in how employers evaluate talent. The focus is increasingly moving away from traditional credentials, such as college degrees, towards a more holistic, skills-based approach. The TestGorilla report reinforces this trend:
- 57% of US employers have dropped college degree requirements.
- 74% use skills tests to assess candidates.
- Only 38% seek AI-specific skills, down from 52% the previous year, suggesting that while AI tools are used, the focus is on foundational human capabilities.
This emphasis on skills reflects the evolving demands of the modern workplace, where adaptability, critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving are paramount. As AI automates routine tasks, the value of uniquely human talents increases. Employers are recognizing that a candidate's ability to learn, adapt, and collaborate is often a better predictor of success than their educational background or even specific technical skills that may quickly become outdated.
Durville emphasizes this point: “Employers want people who can think critically, adapt, and collaborate. That’s why more are investing in tools to assess values, behaviors, and soft skills, not just technical ability. The best hiring strategies now combine objective data with a holistic view of the candidate—their skills, values, and cultural alignment.”
The data supports the importance of this holistic view. According to TestGorilla, 82% of US employers attribute bad hires to a lack of soft skills or poor cultural fit. This highlights the limitations of relying solely on resumes and traditional interviews, which may not effectively assess these crucial attributes.
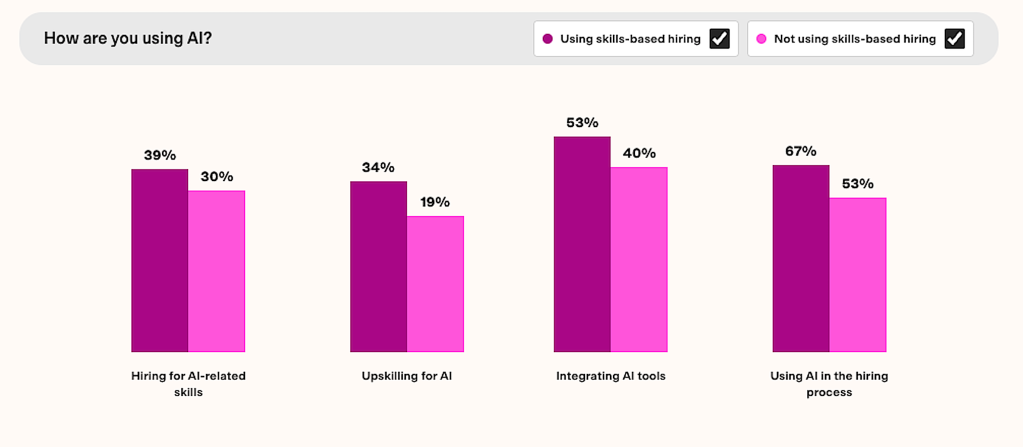
Employers who embrace skills-based hiring are also more likely to be proactive in other areas:
- Hire for AI skills (39% vs. 30% of those not focused on skills).
- Upskill their existing workforce for AI (34% vs. 19%).
- Use AI tools in workflows (53% vs. 40%).
- Use AI in hiring (70%) and specifically for interviews (20%).
This suggests a correlation between a forward-thinking, skills-first approach and a greater willingness to adopt and leverage AI technologies across the organization, including in recruitment.
A report from Indeed further supports the shift, indicating that both employers and job seekers increasingly favor skills-first hiring over traditional degree-based criteria. This alignment between employer strategy and candidate preference could pave the way for more equitable and effective hiring processes.
The Challenge of AI-Generated Applications
Just as employers are adopting AI, so too are job seekers. Candidates are increasingly using generative AI tools to craft resumes, cover letters, and even prepare for interviews. This presents a new challenge for hiring teams: identifying authentic candidate contributions versus AI-generated content.
The TestGorilla survey found that 76% of employers are seeing more AI-generated resumes, and a significant majority (72%) find them relatively easy to spot. Joel Wolfe, president of HiredSupport, a BPO company, corroborates this, noting an increase in easy-to-catch AI-generated resumes and interview responses, particularly in tech roles, characterized by formulaic sentence structures and overuse of buzzwords.
This trend underscores the limitations of relying solely on resumes for candidate evaluation. As AI makes it easier for candidates to optimize their applications for keyword scanning and traditional screening methods, employers are compelled to implement more robust assessment strategies that go beyond the resume. This further strengthens the case for skills tests, behavioral assessments, and structured interviews — methods less susceptible to AI manipulation and better suited for evaluating genuine capabilities and fit.
Implementing AI in Practice: Examples from Industry Leaders
Numerous companies are already demonstrating the practical application of AI in their hiring workflows, showcasing the diverse ways the technology can be leveraged:
- Remote: This HR tech platform recently launched Recruit AI, an AI-infused tool designed for talent sourcing. It accesses a vast database of global candidate profiles and uses natural language processing and advanced filtering to quickly surface tailored candidate batches based on job descriptions, motivations, and eligibility.
- HireVue: Known for its video interviewing software, HireVue uses genAI to screen resumes and prioritize candidates based on job fit and predicted success.
- Unilever: The consumer goods giant famously used HireVue's AI-powered video interviews. Candidates recorded responses to pre-set questions, which the AI analyzed for various cues, leading to significant reductions in hiring time and improvements in diversity metrics before candidates advanced to human interviews.
- IBM: The tech giant has reported substantial productivity gains from using genAI internally, including in HR. IBM's genAI now handles 94% of HR questions, significantly reducing the workload on HR Business Partners.
- Siemens: This tech company has integrated AI into its recruitment processes to enhance efficiency and reduce time-to-hire, using AI for initial interviews and response analysis for quicker shortlisting.
- McDonald's: In the US and Australia, McDonald's has deployed Paradox's chatbot "Olivia" for initial interviews via SMS or mobile web. The chatbot automatically schedules in-person interviews for qualified candidates, accelerating hiring for high-turnover roles.
- Eightfold AI: A leader in talent intelligence, Eightfold AI recently introduced AI Interview for real-time conversational assessments and Digital Twin, a personalized LLM capturing employee skills and experiences. Companies like Tata Communications and Postmates have used Eightfold AI to match candidates based on skills and potential.
These examples demonstrate that AI is being applied across different stages and types of roles, from high-volume frontline positions to specialized tech roles, proving its versatility and potential impact.
Benefits and Challenges of AI Adoption
The primary driver for AI adoption in hiring appears to be efficiency. The TestGorilla data shows that 97% of US employers and 92% of UK employers who use genAI in hiring report efficiency gains. This includes faster screening, quicker interview scheduling, and reduced administrative burden.
Beyond efficiency, proponents argue that AI can lead to more objective and data-driven hiring decisions. By analyzing candidate data based on predefined criteria, AI tools can help mitigate human biases that might unconsciously influence hiring choices. Cliff Jurkiewicz, vice president of global strategy at HR tech firm Phenom, notes that employer skepticism is fading as the proven outcomes of AI become harder to deny. He adds that candidates also benefit from a more engaging, consumer-grade experience.
However, AI in hiring is not without its challenges. The TestGorilla report highlights reasons why some employers (30%) are not yet using AI:
- Lack of perceived importance (44%)
- Cost and complexity of implementation (32%)
- Data security risks (30%)
Another significant concern is the potential for bias within AI algorithms. If the data used to train AI models reflects historical biases present in past hiring decisions, the AI may perpetuate or even amplify those biases, leading to unfair outcomes for certain candidate groups. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI hiring tools is paramount.
Durville acknowledges these challenges: “Of course, AI interviews are still finding their footing. Some companies have reported efficiency gains, while others are working through the quirks of the technology. But as we add more safeguards, transparency, and human oversight — particularly to prevent bias creeping in — we can expect these tools to mature and become a well-used tool for busy hiring teams.”
The issue of candidates using AI to game the system also necessitates careful consideration. While many employers can spot AI-generated applications, the arms race between AI tools used by candidates and those used by employers is likely to continue. This reinforces the need for hiring processes that evaluate candidates through multiple methods, including human interaction and performance-based assessments.
The Future of AI in Hiring: A Hybrid Approach
The trajectory of AI in hiring points towards a future where technology and human expertise work in tandem. AI is proving invaluable for automating initial stages, handling large volumes of data, and identifying potential candidates based on objective criteria and skills. However, human recruiters and hiring managers remain essential for evaluating nuanced aspects like cultural fit, communication style, and complex problem-solving abilities that require human judgment and empathy.
The trend is clear: organizations are moving towards a more well-rounded, multi-measure approach that combines the efficiency and data-driven insights of AI with the critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and relationship-building skills of human professionals. This hybrid model aims to leverage the strengths of both, leading to faster, fairer, and ultimately more effective hiring outcomes.
As Trey Causey, Indeed’s Head of Responsible AI, notes, adopting new AI tools is crucial in the talent industry, acknowledging that the implementation journey may not always be seamless. However, the potential benefits — from enhanced efficiency and reduced bias to improved candidate experience and better quality hires — are driving continued innovation and adoption.
In conclusion, generative AI has firmly established itself as a powerful tool in the modern recruitment arsenal. Its increasing use in initial interviews, coupled with its widespread application in screening and sourcing, signals a fundamental shift in how companies find and evaluate talent. While challenges related to bias and authenticity require ongoing attention, the move towards skills-based hiring, supported by AI and human oversight, promises a more efficient, equitable, and effective future for talent acquisition.
