Asia's Tech Landscape: From Deep Space Probes and AI Knowledge Capture to Digital Control and Infrastructure Expansion
The technological landscape across Asia continues to evolve at a rapid pace, marked by ambitious space exploration, innovative applications of artificial intelligence, complex dynamics of digital control, and significant investments in critical infrastructure. Recent developments highlight the diverse priorities and challenges facing nations and corporations in the region, from reaching for distant celestial bodies to preserving human expertise and shaping the digital information flow.
China's Deep Space Ambitions: Tianwen 2 Unfurls its 'Solar Wing'
China's space program has been making significant strides, and its latest deep space mission, Tianwen 2, is a testament to its growing capabilities. Launched in May, the probe is on an ambitious trajectory designed to visit two distinct remote objects: the 'quasi-moon' asteroid 469219 Kamoʻoalewa and the comet 311P. This dual-target mission underscores China's increasing focus on understanding near-Earth objects, which hold scientific value for studying the early solar system and practical interest for potential resource utilization and planetary defense.
Just eight days after its launch, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) provided its first update on the mission's status. The probe had successfully traveled three million kilometers from Earth, a critical early milestone. A particularly noteworthy detail from the update was the successful deployment of the probe's "solar wing." This isn't a traditional rigid solar panel array but a circular, flexible structure designed to capture solar energy efficiently in the challenging environment of deep space.
The CNSA also shared the first image captured by the probe, offering a glimpse of this deployed solar wing against the backdrop of space. This image, while simple, signifies a crucial step in the mission's readiness, confirming that the spacecraft is powered and operational as it begins its long journey. The successful deployment of such a critical component is a relief for mission planners and a promising sign for the complex maneuvers and scientific observations planned for the years ahead.
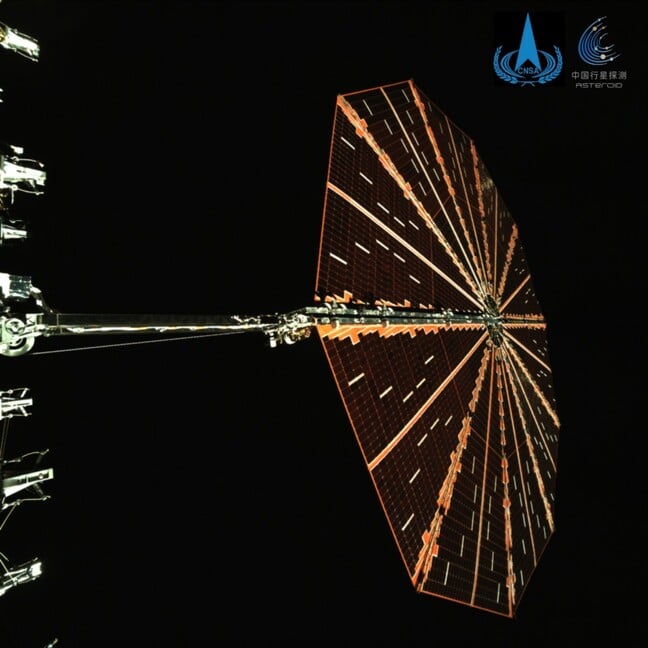
The Tianwen 2 mission follows the success of Tianwen 1, which successfully landed a rover on Mars, demonstrating China's ability to execute complex interplanetary missions. The focus on asteroids and comets with Tianwen 2 aligns with global trends in space exploration, recognizing these objects as potential sources of information about the solar system's formation and evolution, as well as potential future resources. The choice of Kamoʻoalewa, a quasi-satellite of Earth, is particularly interesting, as its unusual orbit could provide insights into objects that interact closely with our planet. Comet 311P, also known as P/2013 P5, is known for its unusual appearance, displaying multiple tails, suggesting complex activity. Studying such a comet up close could yield valuable data on cometary processes.
The mission profile for Tianwen 2 is expected to be lengthy and complex, involving rendezvous, potential landing, and sample collection from Kamoʻoalewa, followed by a journey to and study of comet 311P. The successful unfurling of the solar wing is just one of many critical steps required for the probe to maintain power and execute its scientific objectives throughout this multi-year voyage. As the mission progresses, scientists and engineers worldwide will be watching closely, eager for the data and images Tianwen 2 is expected to send back, further expanding humanity's understanding of the small bodies in our solar system.
Bridging the Generational Gap: Hitachi Turns Veteran Expertise into AI Agents
In a rapidly aging society like Japan, preserving the knowledge and expertise of experienced workers before they retire is a significant challenge for many industries. Hitachi Power Solutions is tackling this issue head-on by exploring innovative uses of artificial intelligence to capture and retain the invaluable know-how of its veteran employees. This initiative aims to create AI agents that can serve as digital repositories of experience, accessible to younger generations of workers.
According to a report by Nikkei Asia, Hitachi's approach involves a multi-faceted data collection strategy. They began by analyzing existing logs and operational data generated by their systems and equipment. This provides a baseline of how systems behave and how issues have been addressed historically. However, recognizing that much critical knowledge resides in the minds and practices of long-time employees, the company went further. They conducted in-depth interviews with veteran workers and performed ethnographic research, observing how these experts approach problem-solving and decision-making in real-world scenarios.
The goal is to translate this tacit, often unwritten, knowledge into a format that an AI can learn from and utilize. The result of this effort is a "Maintenance Inquiry AI Agent." This agent is designed to be queried by less experienced workers when they encounter issues while troubleshooting Hitachi's complex equipment. Instead of relying solely on manuals or escalating problems, workers can potentially consult the AI agent to gain insights and guidance based on the collective experience of their senior colleagues.
This project highlights a crucial application of AI beyond typical customer service chatbots or data analysis tools. It addresses a demographic challenge by attempting to create a digital bridge across generations of the workforce. By preserving expertise that might otherwise be lost to retirement, companies can potentially maintain operational efficiency, reduce training time, and ensure consistent quality in maintenance and troubleshooting tasks. The success of such initiatives could pave the way for similar applications in other industries facing similar demographic shifts and knowledge retention challenges.
The development process likely involves techniques from natural language processing (NLP) to understand queries, machine learning to identify patterns in troubleshooting data, and potentially knowledge representation techniques to structure the interview and ethnographic data. The challenge lies not just in collecting the data but in effectively encoding the nuances of human expertise, which often involves intuition, contextual understanding, and practical wisdom gained over years of hands-on experience. Hitachi's project represents a fascinating attempt to bottle this lightning using AI technology.
The Digital Iron Curtain: China's 'Delete First, Review Later' Censorship Policy
China maintains one of the most extensive and sophisticated internet censorship regimes in the world, often referred to as the Great Firewall. The state's control over online information is particularly intensified around politically sensitive dates and events, such as the anniversary of the Tiananmen Square massacre on June 4th. Recent reports, based on leaked internal documents, shed further light on the mechanisms and directives guiding this vast censorship apparatus.
A report from the Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC), citing leaked documents from within Beijing's censorship operations, revealed training materials and internal memos for internet censors. These documents reportedly include explicit instructions to remove content depicting state violence and provide examples of forbidden text, images, and video related to sensitive topics like the 1989 crackdown.
Perhaps most revealing is an internal memo suggesting a "delete first, review later" approach to censorship. This directive indicates a bias towards caution and control, prioritizing the swift removal of potentially problematic content over a thorough review process. This approach minimizes the risk of forbidden information circulating, even if it means temporarily removing legitimate content. It underscores the proactive and often heavy-handed nature of China's digital control.
The leaked documents also highlight the scale and organization of the censorship workforce, often involving thousands of individuals employed by technology companies under state direction. These human censors work alongside increasingly sophisticated AI tools designed to automatically detect and flag sensitive keywords, images, and even video content. The combination of human oversight and AI automation allows the authorities to process vast amounts of online data and enforce censorship directives at scale.
The period around the Tiananmen anniversary is consistently marked by heightened censorship activity. This year was no exception, with authorities working diligently to scrub any mention or oblique reference to the events of 1989 from Chinese social media platforms, search results, and news sites. However, anti-censorship organizations continue to find ways to challenge these controls.
For instance, the Chinese anti-censorship group GreatFire, in collaboration with the Human Rights Museum, undertook a project aimed at making information about the Tiananmen Square massacre accessible to Chinese netizens despite the Great Firewall. Such projects often employ creative technical workarounds, like mirroring blocked websites on uncensored platforms or using decentralized networks, to bypass state controls. While these efforts face constant challenges from the authorities, they represent a persistent pushback against the state's monopoly on information.
The leaked documents and the ongoing cat-and-mouse game between censors and anti-censorship activists illustrate the complex and tightly controlled information environment within China. The "delete first, review later" policy reveals a system designed for maximum control, where the potential harm of forbidden information is deemed far greater than the inconvenience or impact of over-censorship. This has profound implications for freedom of expression, access to information, and the development of a truly open digital public sphere within the country.
Infrastructure Backbone: Equinix Expands Data Center Footprint in the Philippines
As digital economies grow and cloud adoption accelerates across Asia, the demand for robust data center infrastructure continues to surge. Global data center giant Equinix recently announced a significant expansion of its presence in Southeast Asia through the acquisition of three data centers from Total Information Management (TIM) in the Philippines.
The acquisition includes three facilities located in Manila, the capital city and a major economic hub of the Philippines. These data centers collectively add a capacity of 1,000 cabinets to Equinix's portfolio in the region. Crucially, the deal also includes land for further expansion, signaling Equinix's intent to grow its capacity in the Philippines beyond the initial acquisition.
The newest of the acquired facilities, known as MN2, contributes 500 cabinets to the total capacity, indicating it is a more modern and larger-scale facility compared to the others. This acquisition allows Equinix to immediately bolster its offerings in the Philippine market, providing essential interconnection and colocation services to both local enterprises and international companies looking to establish or expand their digital presence in the country.
Equinix highlighted that acquiring these operational data centers enables them to "immediately support local and global customers looking to expand into the Philippines." This is a strategic move, as building new data centers from the ground up can be a lengthy process involving site selection, permitting, construction, and commissioning. By acquiring existing facilities, Equinix gains a quicker path to market and an established customer base.
The Philippines is an increasingly attractive market for data center investment due to its large population, growing digital economy, increasing internet penetration, and strategic location in Southeast Asia. The demand for cloud services, online content, and digital financial services is driving the need for localized data center capacity that can offer low latency and high reliability.
Equinix specializes in providing highly interconnected data centers, known as International Business Exchange (IBX) data centers, where companies can connect directly to a dense ecosystem of networks, cloud providers, and business partners. Expanding this ecosystem into the Philippines will be beneficial for businesses operating in or expanding to the country, enabling faster and more efficient digital operations.
This acquisition is part of a broader trend of global data center operators investing heavily in the APAC region to meet the escalating demand for digital infrastructure. The Philippines, like other emerging markets in Southeast Asia, represents a significant growth opportunity for companies like Equinix as digital transformation initiatives accelerate across various sectors.
Boosting Developer Productivity: Samsung Adopts AI Coding Tool Cline
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being integrated into various professional workflows, and software development is no exception. AI-powered coding assistants are becoming popular tools for developers, promising to enhance productivity and streamline the coding process. Samsung's Device eXperience (DX) division has reportedly adopted the Cline AI coding assistant, signaling a move towards leveraging AI in the development of its consumer electronics.
According to Korean media reports, the DX division, responsible for developing Samsung's wide range of products including mobile devices (like the Galaxy smartphones), home appliances, and televisions, has integrated Cline into its development environment. This suggests that AI is now playing a role in the creation of the software that powers millions of Samsung devices worldwide.
The report also notes that Cline works alongside Microsoft's Visual Studio Code (VS Code), a popular free source-code editor. This detail provides a hint about the development tools and environment used within Samsung's DX division. The integration of an AI assistant like Cline into a widely used editor like VS Code is a common pattern for such tools, aiming to provide assistance directly within the developer's workflow.
AI coding assistants typically offer features such as code completion, suggesting lines or blocks of code based on context; code generation, writing functions or snippets based on natural language descriptions; bug detection and suggestion of fixes; and code refactoring. By automating repetitive tasks and providing intelligent suggestions, these tools can potentially free up developers to focus on more complex problems and creative aspects of software design.
Samsung's adoption of Cline reflects a broader industry trend where technology companies are exploring and implementing AI tools to improve developer efficiency and code quality. While the specific capabilities of Cline are not detailed in the source, its adoption by a major division responsible for a diverse product portfolio suggests a belief in the potential benefits of AI assistance in large-scale software development projects.
The integration of AI into the development process raises interesting questions about the future of software engineering. While AI assistants can significantly boost productivity, they also introduce considerations around code ownership, security (especially when using cloud-based AI models), and the potential for propagating errors or biases present in the training data. Nevertheless, the move by a technology giant like Samsung indicates that AI coding tools are moving from experimental use to becoming standard components of the development toolkit.
As AI coding tools become more sophisticated, they could transform how software is built, potentially accelerating development cycles and enabling smaller teams to achieve more. Samsung's decision to adopt Cline is a notable step in this direction within the consumer electronics space, highlighting the increasing reliance on AI across various facets of the technology industry.
Cloud Expansion: AWS Launches New Region in Taiwan
Cloud computing infrastructure is fundamental to the global digital economy, providing the scalable and flexible resources needed for everything from streaming services to enterprise applications and AI model training. Amazon Web Services (AWS), a leading cloud provider, has further expanded its global footprint by launching a new cloud region in Taiwan.
The new region, designated ap-east-2, is located in Taiwan and offers three Availability Zones. Availability Zones are distinct physical locations within an AWS Region that are engineered to be isolated from failures in other Availability Zones. By running applications across multiple Availability Zones, customers can achieve higher levels of fault tolerance and resilience than would be possible from a single data center.
The decision to launch a region in Taiwan is strategically significant. Taiwan is a global hub for technology manufacturing, particularly in the semiconductor industry, and has a vibrant domestic tech sector. Establishing a local cloud region allows Taiwanese businesses and government agencies to run workloads with lower latency and meet data residency requirements. It also provides international companies operating in Taiwan with local cloud infrastructure.
AWS specifically noted that offering three Availability Zones in Taiwan is a "sensible precaution" given the country's frequent experience with earthquakes. Taiwan is located in a seismically active zone, and earthquakes have previously caused disruptions to critical infrastructure, including the operations of major tech companies like TSMC, the world's largest contract chip manufacturer. Building infrastructure across multiple, geographically separated zones within the region helps mitigate the risk of downtime caused by natural disasters or other localized disruptions.
The launch of the Taiwan region is part of AWS's ongoing global expansion to bring cloud infrastructure closer to customers. Having a local region reduces latency for end-users and applications, which is crucial for performance-sensitive workloads like gaming, real-time data processing, and certain enterprise applications. It also supports digital transformation efforts by providing local access to AWS's broad portfolio of services, including compute, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, and AI.
Furthermore, the presence of a local cloud region can support the growth of the local tech ecosystem, providing startups and established businesses with the infrastructure needed to innovate and scale. It can also facilitate digital government initiatives and support industries with specific regulatory or compliance requirements regarding data location.
The investment in a new cloud region in Taiwan underscores the strategic importance of the market for global cloud providers and reflects the increasing demand for digital infrastructure in the APAC region. By providing resilient, low-latency cloud services, AWS aims to support the continued growth and digital transformation of businesses and organizations across Taiwan.
Connecting the Threads: Innovation, Control, and Infrastructure in Asia
The seemingly disparate developments discussed – a deep space probe, AI for knowledge retention, state censorship, data center expansion, AI coding tools, and cloud region launches – are all interconnected threads in the complex tapestry of Asia's technological advancement. They reflect a region that is simultaneously pushing the boundaries of scientific exploration, grappling with the societal implications of AI, navigating the challenges of digital governance and control, and building the foundational infrastructure necessary for future growth.
China's space program, exemplified by Tianwen 2, showcases a nation investing heavily in high-profile scientific and technological endeavors that project national power and inspire future generations. This ambition in space contrasts sharply with the state's tight control over the digital space back on Earth, where censorship mechanisms are becoming increasingly sophisticated, employing both human and AI resources to manage information flow and suppress dissent, particularly around sensitive historical events.
Meanwhile, countries like Japan are exploring practical applications of AI to address unique demographic challenges, such as preserving the expertise of an aging workforce. Hitachi's initiative to turn veteran knowledge into AI agents is a pragmatic response to a real-world problem, demonstrating how AI can be applied to enhance human capabilities and ensure continuity in critical industries.
Across the region, the foundational layers of the digital economy are being strengthened through massive investments in data centers and cloud infrastructure. Equinix's expansion in the Philippines and AWS's new region in Taiwan are critical steps in meeting the surging demand for computing power, storage, and connectivity driven by cloud adoption, AI workloads, and the proliferation of digital services. These infrastructure developments are essential enablers of technological progress and economic growth.
The adoption of AI tools like Cline by major corporations such as Samsung highlights the integration of AI into the very process of creating technology. As AI assists developers in writing code, it has the potential to accelerate innovation cycles across the board, from consumer electronics to enterprise software.
Taken together, these developments paint a picture of a dynamic and complex technological landscape in Asia. It is a region where cutting-edge research and development coexist with stringent state control, where demographic shifts are driving innovative AI applications, and where the foundational digital infrastructure is being rapidly built out to support future growth. Understanding these diverse trends is key to appreciating the trajectory of technology and its impact on societies across this vital part of the world.
The narrative of technology in Asia is not monolithic. It is shaped by national priorities, economic forces, geopolitical considerations, and societal values. From the vast emptiness of space to the intricate circuits of a smartphone and the complex algorithms governing online information, technology is playing a transformative role, presenting both immense opportunities and significant challenges for the billions of people who call this region home.
